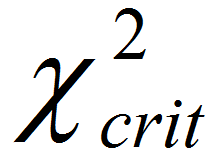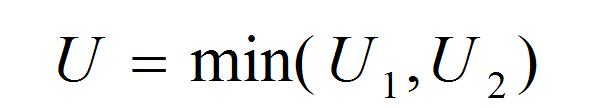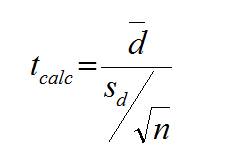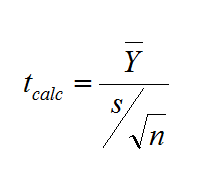What is Stepwise Regression? Stepwise regression is a statistical method to automatically select regression models with the best sets of predictive variables from a large set of potential variables. There are different statistical methods used in stepwise regression to evaluate the potential variables in the model: Three Approaches to Stepwise Regression How to Use Minitab […]