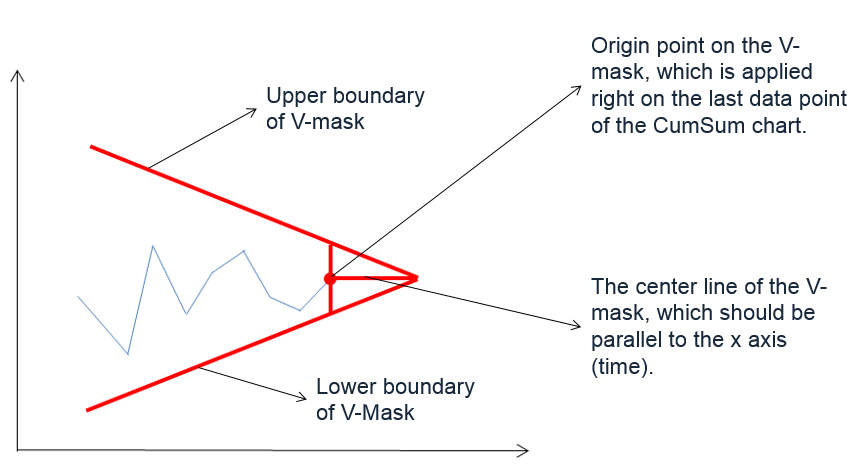
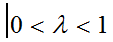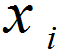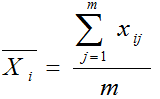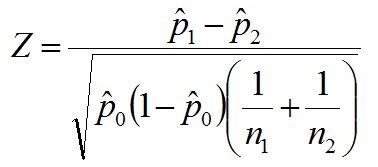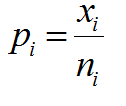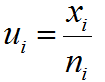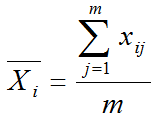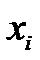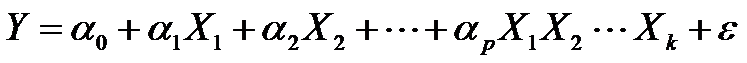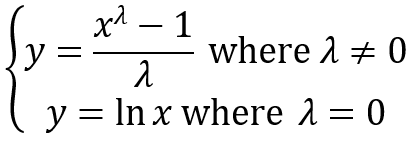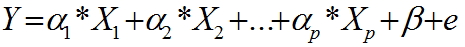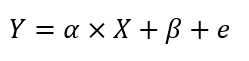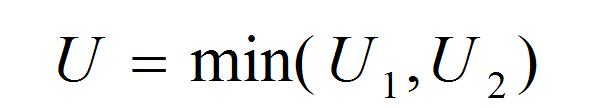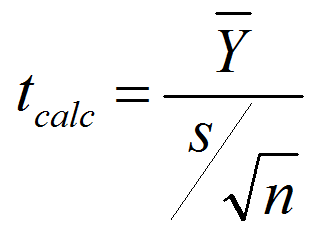What is an EWMA Chart? The EWMA chart (Exponentially-Weighted Moving Average Chart) is a control chart monitoring the exponentially-weighted average of previous and present subgroup means. The more recent data get more weight than older data. It detects the shift of the process mean from the process target over time. The underlying distribution of the […]