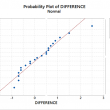
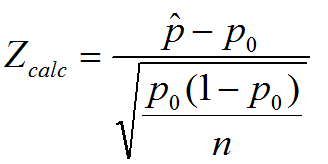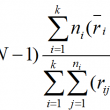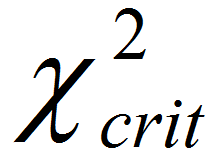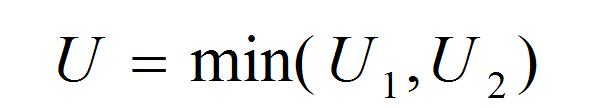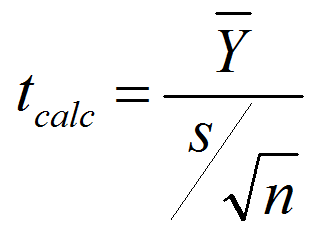What is the One Sample Proportion Test? One sample proportion test is a hypothesis test to compare the proportion of one certain outcome (e.g. the number of successes per the number of trials, or the number of defects per the total number of opportunities) occurring in a population following the binomial distribution with a specified […]